Note
Go to the end to download the full example code.
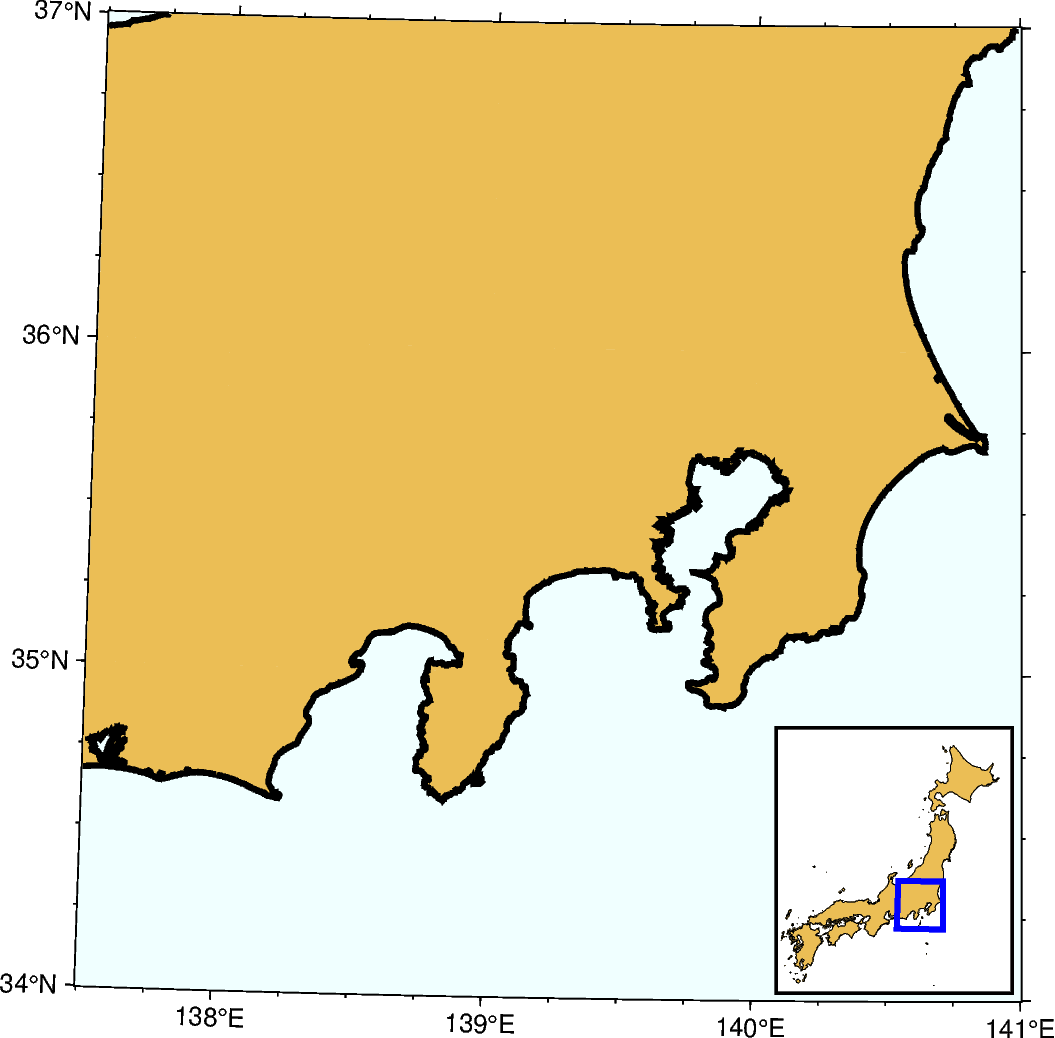
Inset map showing a rectangular region
The pygmt.Figure.inset method adds an inset figure inside a larger figure. The
method is called using a with statement. Plotting methods called within the with
statement plot into the inset figure.
import pygmt
from pygmt.params import Box, Position
# Set the region of the main figure
region = [137.5, 141, 34, 37]
fig = pygmt.Figure()
# Plot the base map of the main figure. Universal Transverse Mercator (UTM) projection
# is used and the UTM zone is set to be "54S".
fig.basemap(region=region, projection="U54S/12c", frame=["WSne", "af"])
# Set the land color to "lightbrown", the water color to "azure1", the shoreline width
# to "2p", and the area threshold to 1000 km^2 for the main figure.
fig.coast(land="lightbrown", water="azure1", shorelines="2p", area_thresh=1000)
# Create an inset map, placing it in the Bottom Right (BR) corner with x- and y-offsets
# of 0.1 cm, respectively. The inset map contains the Japan main land. "U54S/3c" means
# UTM projection with a map width of 3 cm. The inset width and height are automatically
# calculated from the specified ``region`` and ``projection`` parameters. Draws a
# rectangular box around the inset with a fill color of "white" and a pen of "1p".
with fig.inset(
position=Position("BR", offset=0.1),
box=Box(fill="white", pen="1p"),
region=[129, 146, 30, 46],
projection="U54S/3c",
):
# Highlight the Japan area in "lightbrown" and draw its outline with a pen of "0.2p"
fig.coast(dcw="JP+glightbrown+p0.2p", area_thresh=10000)
# Plot a rectangle ("r") in the inset map to show the area of the main figure.
# "+s" means that the first two columns are the longitude and latitude of the bottom
# left corner of the rectangle, and the last two columns the longitude and latitude
# of the upper right corner.
rectangle = [[region[0], region[2], region[1], region[3]]]
fig.plot(data=rectangle, style="r+s", pen="2p,blue")
fig.show()
Total running time of the script: (0 minutes 0.297 seconds)